.
Condición fitosanitaria: Presente
Grupo de cultivos: Cereales
Especie hospedante: Cebada (Hordeum vulgare; Hordeum vulgare var. distichon (L.) Hook.f., 1896)
Rango de hospedantes: específico / estrecho
Etiología: Hongo. Biotrófico
Agente causal: Puccinia hordei Otth
Taxonomía: Fungi > Basidiomycota > Pucciniomycotina > Pucciniomycetes > Pucciniales > Pucciniaceae > Puccinia
.
Antecedentes
Es observada principalmente en zonas templadas. Es la más común de las royas. Las plantas afectadas producen menor número y peso de granos. Desde el 2004 se observa un significativo incremento de su prevalencia e intensidad en Argentina y Uruguay. En Brasil, es una enfermedad muy destructiva.
.
Síntomas y signos
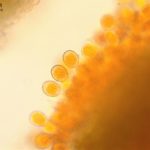
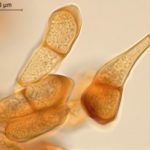
Pústulas pequeñas pulverulentas de color naranja principalmente en la cara superior de las hojas. Posteriormente, aparecen pústulas de color negro en forma de polvillo negro. La enfermedad es más evidente desde fin de macollaje a encañazón.
.
.
Ciclo de la enfermedad
La infección puede comenzar desde la aparición de las primeras hojas. La principal fuente de inóculo son las plantas guachas. La diseminación dentro del cultivo y a distancia, se produce por el viento. El patrón de distribución en el lote es generalizado y uniforme.
.
Condiciones predisponentes
Temperaturas óptimas entre 15 y 22 ºC, asociada con 6-8 horas de mojado foliar. El tiempo, relativamente templado y húmedo.
.
Manejo
* Evitar el uso de cultivares susceptibles. Se han encontrado fuentes de resistencia (Amouzoune et al., 2021; Mehnaz et al., 2021; Singh et al., 2021)
* Evitar la excesiva fertilización nitrogenada
* Evitar altas densidades de plantas
.
.
- 01 Roya de la cebada, causada por Puccinia hordei.
- Autor: Zacharias-Pretorius
- Autor: Zacharias-Pretorius
- Autor: Zacharias-Pretorius
- Autor: Zacharias-Pretorius
.
.
.
Videos
Rust: the fungi that attacks plants. Created by Chris Hammang, Producer Sean O’Donoghue, Scientific Consultant Peter Dodds. C SIRO (Video)
.
.
.
.
Bibliografía
Amouzoune M, Amri A, Benkirane R, et al. (2021) Mining and predictive characterization of resistance to leaf rust (Puccinia hordei Otth) using two subsets of barley genetic resources. Genet Resour Crop Evol. doi: 10.1007/s10722-021-01268-4
Bernardo L, Prinsi B, Negri AS, et al. (2012) Proteomic characterization of the Rph15 barley resistance gene-mediated defence responses to leaf rust. BMC Genomics 13: 642. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-642
Dean R, Van Kan JAL, Pretorius ZA, et al. (2012) The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Molecular Plant Pathology 13: 414–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00783.x
Dinh HX, Singh D, Gomez de la Cruz D, et al. (2022) The barley leaf rust resistance gene Rph3 encodes a predicted membrane protein and is induced upon infection by avirulent pathotypes of Puccinia hordei. Nat Commun 13: 2386. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29840-1
Kavanagh PJ, Singh D, Bansal UK, Park RF (2017) Inheritance and characterization of the new and rare gene Rph25 conferring seedling resistance in Hordeum vulgare against Puccinia hordei. Plant Breeding 136: 908–912. doi: 10.1111/pbr.12535
Lintz J, Dubrulle G, Cawston E, et al. (2022) A Short Review of Anti-Rust Fungi Peptides: Diversity and Bioassays. Front. Agron. 4: 966211. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2022.966211
Marcel TC, Gorguet B, Ta MT, et al. (2008) Isolate specificity of quantitative trait loci for partial resistance of barley to Puccinia hordei confirmed in mapping populations and near‐isogenic lines. New Phytologist, 177: 743-755. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02298.x
Mehnaz M, Dracatos P, Pham A, et al. (2021) Discovery and fine mapping of Rph28: a new gene conferring resistance to Puccinia hordei from wild barley. Theor Appl Genet. 134(7): 2167-2179. doi: 10.1007/s00122-021-03814-1
Sapkota R, Jørgensen LN, Boeglin L, et al. (2021) Under Attack: Fungal Landscape of Spring Barley From Seedling Emergence to Harvest During a Severe Puccinia hordei Epidemic. PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-1007499/v1
Singh L, Park RF, Dracatos P, et al. (2021) Understanding the expression and interaction of Rph genes conferring seedling and adult plant resistance to Puccinia hordei in barley. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology. doi: 10.1080/07060661.2021.1936649
Skoppek CI, Punt W, Heinrichs M, et al (2021) The barley HvSTP13GR mutant triggers resistance against biotrophic fungi. Molecular Plant Pathology 00: 1– 13. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13161
Spelman Z, Visser B, Terefe T, et al. (2022) Pathogenicity and microsatellite characterization of Puccinia hordei in South Africa. Crop Protection 158: 106014. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2022.106014
Vatter T, Maurer A, Perovic D, et al. (2018) Identification of QTL conferring resistance to stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. hordei) and leaf rust (Puccinia hordei) in barley using nested association mapping (NAM). PLoS ONE 13(1): e0191666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191666
Yahyaoui AH, Sharp EL, Reinhold M (1988) New sources of resistance to Puccinia hordei in barley land race cultivars. Phytopathology 78: 905-908. Link
Yeo FK, Wang Y, Vozabova T, et al. (2016) Haplotype divergence and multiple candidate genes at Rphq2, a partial resistance QTL of barley to Puccinia hordei. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 129(2): 289-304. doi: 10.1007/s00122-015-2627-5
Zhang H-S, De La Rosa R, Rubiales D, et al. (1994) Role of partial resistance to Puccinia hordei in barley in the defence of barley to inappropriate rust fungi. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 45(3): 219-228. doi: 10.1016/S0885-5765(05)80079-7
Ziems LA, Hickey LT, Platz GJ, et al. (2017) Characterization of Rph24: A Gene Conferring Adult Plant Resistance to Puccinia hordei in Barley. Phytopathology 107(7): 834-841. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-08-16-0295-R