.
Condición fitosanitaria: Presente
Grupo de cultivos: Hortícolas
Especie hospedante: Poroto (Phaseolus vulgaris)
Etiología: Hongo. Necrotrófico (Hemibiotrófico)
Agente causal: Colletotrichum lindemuthianum (Sacc. & Magnus) Briosi & Cavara, 1889
Taxonomía: Fungi > Ascomycota > Pezizomycotina > Sordariomycetes > Glomerellales > Glomerellaceae > Colletotrichum
.
.
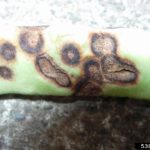
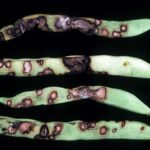
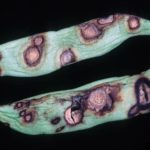
Sintomatología
- Autor: Elizabeth Bush, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Bugwood.org
- Autor: Elizabeth Bush, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Bugwood.org
- Autor: Howard F. Schwartz, Colorado State University, Bugwood.org
- Autor: Gerald Holmes, Strawberry Center, Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, Bugwood.org
- Autor: Gerald Holmes, Strawberry Center, Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, Bugwood.org
.
.
.
.
Bibliografía
Barcelos QL, Pinto JMA, Vaillancourt LJ, Souza EA (2014) Characterization of Glomerella Strains Recovered from Anthracnose Lesions on Common Bean Plants in Brazil. PLoS ONE 9(3): e90910. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090910
, , , et al. (2022) Genome evolution and transcriptome plasticity associated with adaptation to monocot and eudicot plants in Colletotrichum fungi. bioRxiv 2022.09.22.508453; doi: 10.1101/2022.09.22.508453
da Silva CM, Costa LC, Porto ACM, et al. (2021) Differential gene expression in common bean during interaction with race 65 of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Trop. plant pathol. 46: 518–527.
Oliveira MC, Dos Santos GQ, Teixeira JA, et al. (2022) The AbcCl1 transporter of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum acts as a virulence factor involved in fungal detoxification during common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) infection. Braz J Microbiol. doi: 10.1007/s42770-022-00787-1
Reveglia P, Agudo-Jurado FJ, Barilli E, et al. (2023) Uncovering Phytotoxic Compounds Produced by Colletotrichum spp. Involved in Legume Diseases Using an OSMAC–Metabolomics Approach. Journal of Fungi. 9(6): 610. doi: 10.3390/jof9060610
Talhinhas P, Baroncelli R (2021) Colletotrichum species and complexes: geographic distribution, host range and conservation status. Fungal Diversity 110: 109–198. doi: 10.1007/s13225-021-00491-9