.
Condición fitosanitaria: Plaga Cuarentenaria Ausente
Grupo de cultivos: Frutales
Rango de hospedantes: Ampio, no específico, Cientos a miles de especies, incluyendo cutlivos extensivos de grano, pastos, hortalizas, frutales y numerosas malezas.
Especie hospedante: Banano (Musa × paradisiaca L.)
.
Agente causal:
Radopholus similis (Cobb, 1893)
Meloidogyne spp. (~100 species)
.
Taxonomía:
Eukaryota > Opisthokonta > Metazoa > Eumetazoa > Bilateria > Protostomia > Ecdysozoa > Nematoda > Chromadorea > Rhabditida > Tylenchina > Tylenchomorpha > Tylenchoidea > Pratylenchidae > Radopholinae > Radopholus
Eukaryota > Opisthokonta > Metazoa > Eumetazoa > Bilateria > Protostomia > Ecdysozoa > Nematoda > Chromadorea > Rhabditida > Tylenchina > Tylenchomorpha > Tylenchoidea > Meloidogynidae > Meloidogyninae > Meloidogyne > Meloidogyne incognita group
.
.
.
Síntomas
- Plátanos caídos debido a la infección por nematodos y anclaje reducido del sistema de raíces del banano debido a Radopholus similis en Kenia (a) y en Martinica (b). Autor: D. Coyne y P. Quénéhervé, publicado en Sikora et al. 2018
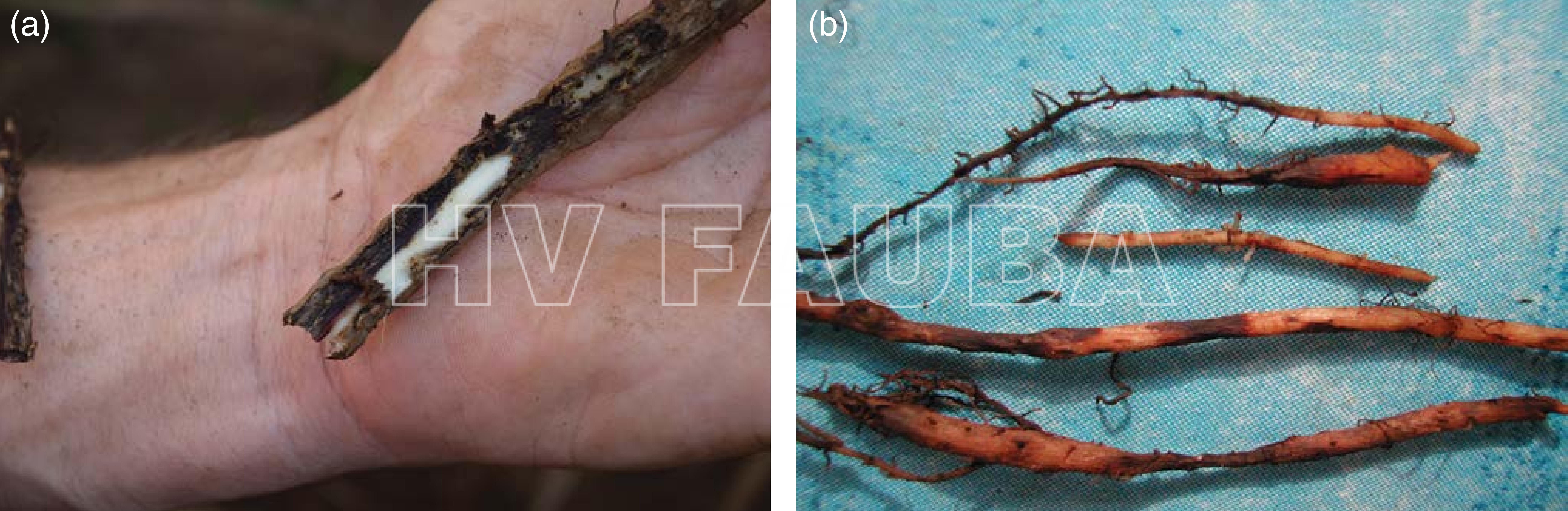
- Raíces de banano lesionadas, infectadas con nematodos, cortadas longitudinalmente (a) y enteras, mostrando necrosis, que penetra en toda la corteza pero no en la estela (b). Autor: D. Coyne, publicado en Sikora et al., 2018.
.
.
Bibliografía
Furtado LL, Rego-Machado Cd, Peixoto GHS, et al. (2023) Polyphasic identification of surgacane root-knot nematodes from ten municipalities in São Paulo State, Brazil. Trop. plant pathol. 48: 523–533. doi: 10.1007/s40858-023-00590-9
Jain A, Huston DC, Wainer J, et al. (2023) Geographic range extension of hop cyst nematode, Heterodera humuli, from Tasmania to the Australian mainland. Australasian Plant Dis. Notes 18: 8. doi: 10.1007/s13314-023-00494-2
Kumar A, Fitoussi N, Sanadhya P, et al. (2023) Two Candidate Meloidogyne javanica Effector Genes, MjShKT and MjPUT3: A Functional Investigation of Their Roles in Regulating Nematode Parasitism. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 36(2): 79-94. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-10-22-0212-R
Lüdke D, Sakai T, Kourelis J, et al. (2023) A root-specific NLR network confers resistance to plant parasitic nematodes. bioRxiv 2023.12.14.571630; doi: 10.1101/2023.12.14.571630
Sikora R, Coyne D, Quénéhervé P (2018) Nematode parasites of bananas and plantains. In: Plant Parasitic Nematodes in Subtropical and Tropical Agriculture (eds RA Sikora et al.). © CAB International. doi: 10.1079/9781786391247.0617
, , (2023) Metabolic variations in root tissues and rhizosphere soils of weak host plants potently lead to distinct host status and chemotaxis regulation of Meloidogyne incognita in intercropping. Molecular Plant Pathology 00: 1–16. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13396